Definition
It is defined as the average poverty gap in the population as a proportion of the poverty line.
· The poverty gap index, sometimes referred to as poverty gap ratio or PG index,
· The poverty gap index is a measure of the
intensity of poverty.
· The poverty gap index is an improvement over the
poverty measure headcount ratio
which simply counts all the people below a poverty line, in a given population,
and considers them equally poor.
· Poverty gap index estimates the depth of poverty
by considering how far, on the average, the poor are from that poverty line
Significance
·
Poverty
gap index provides a clearer perspective on the depth of poverty.
· It
enables poverty comparisons.
· It
also helps provide an overall assessment of a region's progress in poverty
alleviation and the evaluation of specific public policies or private
initiatives
The poverty gap index (PGI) is calculated as,
or
-

- where
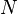 is the total population,
is the total population,  is the total population of poor who are living at or below the poverty line,
is the total population of poor who are living at or below the poverty line,  is the poverty line, and
is the poverty line, and  is the income of the poor individual
is the income of the poor individual  . In this calculation, individuals whose income is above the poverty line have a gap of zero.
. In this calculation, individuals whose income is above the poverty line have a gap of zero. - By definition, the poverty gap index is a percentage between 0 and 100%. Sometimes it is reported as a fraction, between 0 and 1. A theoretical value of zero implies that no one in the population is below the poverty line. A theoretical value of 100% implies that everyone in the population has zero income. In some literature, poverty gap index is reported as
 while the headcount ratio is reported as
while the headcount ratio is reported as 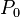
Features
· The poverty gap index can be interpreted as the
average percentage shortfall in income for the population, from the poverty
line
· If you multiply a country's poverty gap index by
both the poverty line and the total number of individuals in the country you
get the total amount of money needed to bring the poor in the population out of
extreme poverty and up to the poverty line, assuming perfect targeting of transfers
· The poverty gap index is an important measure
beyond the commonly used headcount ratio.
· Two regions may have the similar headcount
ratio, but distinctly different poverty gap indexes.
· A higher poverty gap index means that poverty is
more severe.
· The poverty gap index is additive.
· The index can be used as an aggregate poverty
measure, as well as decomposed for various sub-groups of the population, such
as by region, employment sector, education level, gender, age or ethnic group.
Limitations
·
Poverty
gap index ignores the effect of inequality between the poor.
· It
does not capture differences in the severity of poverty amongst the poor.
Source: Wikipedia click here for
article link

 Karthik S.M.K
Karthik S.M.K

Thank you sir
ReplyDelete